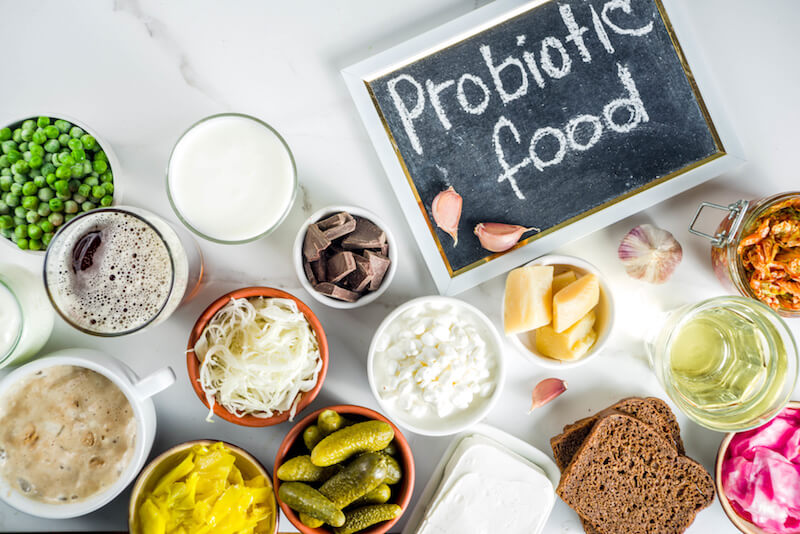
As many embark on a new year diet, I want to tackle the proverbial ‘elephant in the room’: the trillions of bacteria, fungi and viruses that we co-exist with. Consider the fact that we at only around 43% human and 57% microbial, how can we possibly ignore them?!
These microbes are also the reason why so many fad diets fail. What worked for the diet book author, your friend, or your family member, won’t necessarily work for you. Not unless you evolved in a clinically-sealed petri dish with the same shared dietary, social and environmental experiences. Realistically, it just isn’t possible and here’s why… let’s look at the science.
The majority of microbes inhabit our large intestine and every gut microbiome is wholly unique. Think of your gut microbiome like a biological fingerprint or signature. It is the embodiment of all our genetic, physical, mental, emotional, environmental, social, and cultural experiences. What we eat, our belief systems, movement, environment, nature, social and community engagement have all been found to influence the state of our microbiome in research studies.
The human intestinal tract harbours an estimated three trillion bacterial members, up to a 1000 different bacteria species, and the ratio of gut microbiota to human cells is roughly 1:1. What’s more, the genetic diversity of gut microbiota is 100 times higher than that of human cells. That’s a huge amount of DNA we are carrying in us with an infinite numbers of variables possible between person to person.
In the exciting field of nutrigenomics, the focus is on gene expression, whether we activate a particular gene or not. Professor Vittorio Sebastiano, Epigeneticist at Stanford University says as much as 70% of our health outcomes are down to how we live, and not the ‘deterministic’ genes we inherited. The biggest influencer of gene expression is what we eat. However it doesn’t just stop there, as what we eat and how we live doesn’t just affect our DNA, but also the genes of the trillions of bacteria in our gut. The DNA scale and potential is huge, mind-boggling! The main takeaway I want to share however, is that there is a a HUGE amount we can do by means of what we eat and, as Professor Sebastiano says, “much of our destiny truly is in our hands.”
There can be no “one size fits all diet
Even identical twins have been found to not process food the same way. The largest ongoing scientific nutrition study of its kind, explored how more than 1000 participants (around 60 percent were sets of identical twins) process their meals. Surprisingly, the researchers found that even identical twins respond very differently to fats and carbohydrates. The study was carried out by researchers from King’s College London, Massachusetts General Hospital and nutritional science company ZOE, co-founded by Professor Tim Spector, Professor of Genetic Epidemiology at King’s College London.
The results also suggested that personal differences in metabolism due to factors such as the gut microbiome, meal timing and exercise are just as important as the nutritional composition of foods. What fascinates me is that the study found twins shared only 37% of the same microbes with each other. That’s just a little more than unrelated individuals who share an average of 35% of the same microbes.
A successful diet therefore requires an entirely personalised and person-centred or holistic approach. We really are all unique and that’s why I am passionate about supporting my clients in becoming their “own expert”. To help them tune into their own body, the many signs and symptoms that present, and to understand their own individual dietary needs. The focus has to be on sustainable wellness and more often than not, I am putting foods back into my clients’ diets.
Every gut microbiome is wholly unique. Think of it like a biological fingerprint or signature. Truly the embodiment of all our individual DNA, our genetic, physical, mental, emotional, environmental, social, and cultural experiences.
Our DNA originally determines our microbiota. We’re first exposed to microorganisms as an infant, during delivery in the birth canal and through the mother’s breast milk. Later, environmental exposures, diet and lifestyle can alter our microbiome to be either beneficial to health or to place us at greater risk for disease.
A varied and diverse diet is key to optimum health and weight loss
Counting calories is very 1999 in dietary terms. In 2023, all the science suggests you should be counting plants.
Numerous science studies show that greater numbers and a more diverse range of good gut bacteria are key to successful weight loss and management. And key to having more good bacteria is to have a diverse and varied diet high in plants and whole foods. This is what our good bacteria feed on.
Indeed, the worst thing for health and weight management is to eat the same food every single day.
Ideally, aim for more than 7 different plants a day and a minimum of 30 different varieties a week. By plants, I mean vegetables, legumes, fruits, shoots, leaves, nuts, seeds, whole grains, herbs and spices, etc.
Sadly, too many diets have a restrictive element and entail cutting out entire food groups which can result in nutritional imbalances and deficiencies. Instead the focus should be on variety and balance. I see a lot of gut health problems stem from people avoiding dairy and carbohydrates especially. In fact, some carbohydrates such as oats provide important sources of resistant starch which can help boost butyrate-producing microbes.
A lot of gut health problems stem from insufficient butyrate. Butyrate is a short chain fatty acid and the main source of fuel for the cells (colonocytes) lining the colon. Butyrate ensures the optimum environment for your gut microbes to flourish. It also helps insulate blood sugar levels and increase insulin sensitivity; helps regulate energy metabolism; has important anti-inflammatory properties; protects against cancer; and prevents obesity. Butyrate increases leptin gene expression. Leptin suppresses food intake, prevents low metabolism, and promotes weight loss. Higher butyrate levels also help increase levels of glutathione, an important antioxidant which helps strengthen the intestinal barrier and increase bioavailability of iron and zinc.
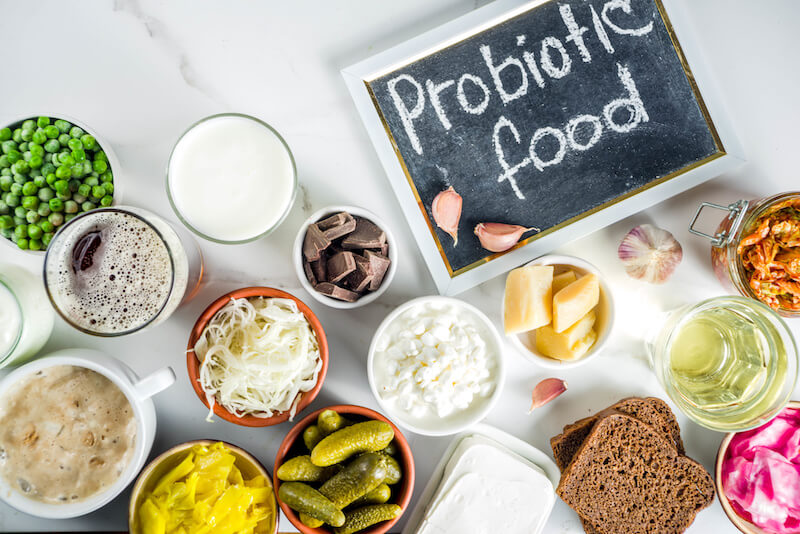
Fermented dairy products like kefir, bio yoghurt and certain probiotic cheeses are important sources of good bacteria (lactobacillus and bifidobacteria).
In cutting out whole food groups, you can unwittingly exclude certain good bacteria which are very beneficial to health and aid weight loss. This isn’t a good idea. More so, when you consider that science research increasingly studies health conditions in relation to the lower incidence or absence of a certain gut microbe.
As for eliminating fat entirely from your diet, extra virgin olive oil is a valuable source of polyphenols which help promote Akkermansia Municiphilia, a beneficial bacteria that helps strengthen the intestinal lining. That lining, our gut epithelium, is the dividing line between the human and microbial worlds, and it plays a critical mediator role. It really is our front line defence to external threats, a key facet of our immune system.
Essential fatty acids such as omega 3 found in oily fish and flaxseeds also have anti-inflammatory properties and are important for vitamin A,D,E, and K absorption, hormonal health, blood sugar and cholesterol management; also gut, brain, liver and heart health. Good fats are also important for bile flow. Insufficient bile is another contributor to so many gut health problems that I see. Yo-yo fasting and low fat diets also risk later gallbladder removal.
Our microbiome plays so many key roles in promoting the smooth everyday operation of the human body. Most of our microbes are symbiotic (where both the human body and microbiota benefit) but some, in smaller numbers, are pathogenic (promoting disease).
In a healthy body, pathogenic and symbiotic microbiota coexist happily. However, if there is a disturbance in that balance—brought on by infectious illnesses, certain diets, or the prolonged use of antibiotics, artificial sweeteners, or other bacteria-destroying medications—gut dysbiosis occurs. This stops the normal interactions and as a result, the body can become more susceptible to disease.
Gut dysbiosis is implicated in various conditions including IBS, allergies, autism, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, type 2 diabetes and obesity.
In particular, a high-fibre diet affects the type and amount of microbiota in the intestines. Dietary fibre can only be broken down and fermented by enzymes from microbiota living in the colon. These bacteria then release short chain fatty acids such as butyrates as a result of the fermentation process. This lowers the pH of the colon, which, in turn, determines the type of microbiota present that would survive in this acidic environment. The lower pH limits the growth of some harmful bacteria like Clostridium difficile.
Our gut microbes aren’t just gate-crashing, they are integral to our health
Our gut microbiota help us:
- Digest food
- Produce metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids and vitamins, which strengthen the gut barrier and regulate/promote a healthy immune system
- Protect us against other pathogenic, disease-causing bacteria
- Break down potentially toxic food compounds
- Synthesise certain vitamins and amino acids, including B vitamins and Vitamin K
- Help regulate our hormones, including the amount of oestrogen circulating in our system at any one time
- Produce neurotransmitters that affect how we feel, including dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid. These are key players in triggering intense feelings of happiness, reward, or anxiety
Indeed, our gut bacteria greatly impact our overall physical, emotional and mental health. It is why I do scientific cognitive testing, anxiety, depression and perceived stress screening, so that clients can objectively measure their progress, Increasingly, research is looking into how our gut bacteria also influence our behaviour.
In 2023, Promote Food Diversity
The first UK Food Diversity Day will be taking place this Friday, on the 13th January. Professor Tim Spector will be taking part in that along with other leading experts. Dan Saladino, author of ‘Eating to Extinction’ has been really driving awareness of this important issue. Saladino’s article ‘Are we eating ourselves to extinction?’ explains why we really should be thinking more about what we put on our plate. What are the implications of the world’s increasingly homogeneous diet for the diversity of our gut microbiota and our overall health?
Here’s a scary statistic: of the 6,000 plant species humans have eaten over time, the world now mostly eats just nine, of which just three – rice, wheat and maize – provide 50% of all calories. Add potato, barley, palm oil, soy and sugar (beet and cane) and you have 75% of all the calories that fuel our species. As thousands of foods have become endangered and extinct, a small number have risen to dominance. For example soy which plays a starring role in an increasingly homogeneous diet eaten by billions of people.
These dietary shifts are taking place on a global level and are unprecedented. Global markets increasingly infringe on our food choices. They threaten the diversity of natural food sources so essential to our gut microbiome. I encourage everyone to incorporate more plants and whole foods in their diet, and to seek out new varieties! Try a new plant this week or try growing it in your garden. Our very future might depend on it.
For more information or to book a nutrition consultation, contact Charlotte Fraser at enquiries@naturopathic-nutrition.com.